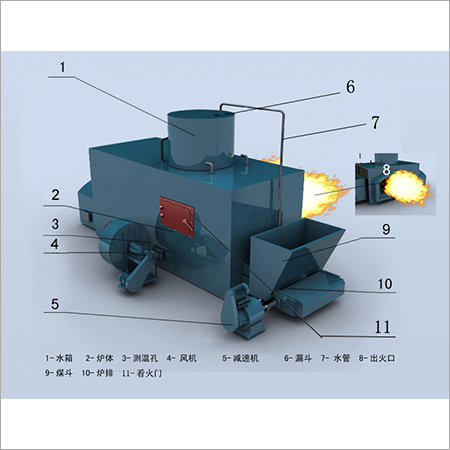
Furnace Manufacturers
(2942 products)Electric Benchtop Muffle Furnace Usage: Industrial
Price: 65000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
UsageIndustrial
ConditionNew
Trf Furnace Application: Industrial
Price: 1000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units,
Size500 Kg
ConditionNew
UsageMelting Furnace
Voltage410 Volt (v)
ApplicationIndustrial
Rotary Klin Furnaces And Incinerator
Price: 35000000 INR/Set
MOQ01 Set/Sets
FOB PortJNPT Nava Sheva Mumbai
Payment TermsLetter of Credit (L/C), Letter of Credit at Sight (Sight L/C), Telegraphic Transfer (T/T)
Supply Ability01 Per Month
Temperature Furnace
Product DescriptionWe are instrumental in providing to our valuable customers excellent quality Temperature Furnace which is available with following Features:-\015\0121. It has stainless steel shell and there are observing holes on the door.\015\0122. It has high-quality refractory materials and the vacuum, forming
Haida International Equipment Co., Ltd.
Dongguan
Reheating Furnace - Cast Iron, Max Temperature 950°C | Semi-Automatic, Frequency Speed Control, Computerized, Durable Design
Price Trend: 100000.00 - 150000.00 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
TypeOther, Reheating Furnace
MaterialCast Iron
ComputerizedYes
Automatic GradeSemi-Automatic
Control SystemFrequency Speed Control
Voltage380-420 Volt (v)
250gm Nano Gold Metro Gold Melting Induction Furnace
Price: 500000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 , Piece/Pieces
Supply Ability2 Per Week
Delivery Time15 Days
Ashlyn Chemunnoor Instruments Pvt. Ltd.
Thrissur
Muffle Furnace - Up to 1200°C Temperature, Digital Controller with 3°C Accuracy | Ideal for I.S. & A.S.T.M. Standards in Research, Medical, and Industrial Applications
Product DescriptionWe manufacture our exclusive range of muffle furnace, which have been specifically designed & fabricated to serve various purposes of I.S. & A.S.T.M. standards application in many fields including metal treatment, ash determination, medical, agricultural, industrial, research laboratories & wool ind
Furnace Roller Bracket
RatingStandard
FeatureDurable and heat-resistant
ConditionNew
TypeRoller Bracket
UsageUsed in furnace rollers for heavy industry, Other
SizeMedium
Muffle Furnace - High-Temperature Resistant | Ideal for Laboratory Applications, Efficient Thermal Control, Durable Design
Price: 35000 INR/Number
MOQ1 Number
Payment TermsCash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
Supply Ability10 Per Week
Delivery Time15 Days
Muffle Furnace - Application: Industrial
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Weight45 Kilograms (kg)
Size23 x 10 x 10mm
Product TypeMuffle Furnace
UsageLaboratory
ColorWhite
ConditionNew
Meta-lab Scientific Industries
Mumbai
Billet Furnace - 15KW to 150KW, 1200°C Maximum Temperature, Water-Cooled High-Temperature Cement Cooled Induction Coil - Pollution Free, High Efficiency, Automation Ready
Price: 270000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units, Unit/Units
Voltage415 Volt (v)
Shapet Induction Private Limited
Rajkot
 Super Seller
Super Seller16 Years
Klinger gasket
Price: 21200 INR/Roll
MOQ5 Roll/Rolls
Size2250mm x1500 mm x3 mm
UsageFurnace shunt insulation
TypeC4300
Therma Field Power Components Private Limited
Ahmedabad
High Temperature Muffle Furnace 1400 Degree Celsius Digital
Product DescriptionHigh Temperature Muffle Furnace 1400 Degree Celsius Digital
230Vac Industrial High Temperature Muffle Furnace Power: 230 Volt (V)
Price: 24000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
UsageIndustrial
FeatureTemperature Control, Digital Display
Product TypeMuffle Furnace
ConditionNew
Type230VAC Industrial High Temperature Muffle Furnace
Power230 Volt (v)
Compact Tube Furnace Application: Industrial
Price: 481000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
ColorGrey
SizeDifferent Available
ConditionNew
TypeCompact Tube Furnace
ApplicationIndustrial
Bishops Scientific Private Limited
Mumbai
K Type Sensor Based Muffle Furnace - 9 x 4 x 4 Inch Chamber, 3000 Watt Power | New Condition, Insulated with Glass Wool, Ambient to 900°C Temperature Range, Includes Essential Accessories
Price: 45000.00 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Weight25 Kilograms (kg)
Length4 Inch (in)
Width4 Inch (in)
Height9 Inch (in)
Size4 inch X 4 inch X 9 inch*
UsageTo determine Percentage of ash in polymers.
Muffle Furnace - High-Temperature Ceramic Build, Precision Temperature Control up to 1200°C, Ideal for Lab Applications
Price: 16500 INR/Unit
MOQ1 , Unit/Units
Supply Ability10 Per Month
Delivery Time1 Days
Main Domestic MarketAll India
Yesha Lab Equipments
Ahmedabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller7 Years
Heat Resistant Trays Normalizing Furnace
Product DescriptionBacked by a team of diligent experts, we have been able to manufacture, export and supply a wide range of Heat Resistant Trays Normalizing Furnace in Faridabad, Haryana, India. Our provided furnaces are extremely desired by our patrons for their fine finish and rugged construction. The offered furna
Aluminium Single Log Heater - Color: Blue
Price: 5300000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
ColorBlue
SizeStandard
Usageindustrial
Product TypeAluminium Single Log Heater
ConditionNew
TypeAluminium Single Log Heater
High Quality Industrial Special Furnace
Price: 27000 INR/Unit
MOQ10 Unit/Units
UsageIndustrial
FeatureHigh Quality
ConditionNew
Muffle Furnace Dimensions: 150 X 150 X 300 Millimeter (Mm)
Price: 80000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Weight100 Kilograms (kg)
UsageIndustrial
ConditionNew
TypeMuffle Furnace
Voltage220/230 Volt (v)
Dimensions150 x 150 x 300 Millimeter (mm)
Southern Scientific Lab Instruments Private Limited
Chennai
Long Service Life Ees Heat Treatment Furnace
Price: 4000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 , Set/Sets
FeatureLong Service Life
SizeAs per requirement
ConditionNew
TypeHeat Treatment Furnace
UsageIndustrial, Other
Dhanaprakash Industrial Corporation
Miraj
Laboratory Muffle Furnace - Application: Heating
Price: 18500.0 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces, Piece/Pieces, Piece/Pieces
ConditionNew
UsageHeat Treatment furnace
Power220 Volt (v)
Voltage220 Volt (v)
Dimensions152.4 x 152.4 x 152.4 Millimeter (mm)
Applicationheating
Aluminium Melting Furnace - Capacity: 300 Kg
Price: 250000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
ConditionNew
UsageIndustrial, Other
Power2 kW Watt (w)
Voltage440 Volt (v)
Capacity300 Kg
Warranty1 Year
Industrial Furnace - High-Temperature Heat Treatment System | Reliable for Annealing, Hardening, Tempering & Stress Relieving Processes
Product DescriptionWe are providing Industrial Furnace to our consumers. These tempering furnaces provide a reliable platform for acquiring various mechanical properties during tempering and reduce the residual stresses during the stress relieving process. These furnaces are also used for Heat Treatment application su
Sensoheat Engineering Equipments (i) Pvt. Ltd
Chikhli
Pellet Burner Dimension(L*W*H): Customizable Inch (In)
Price Trend: 20000.00 - 200000.00 USD ($)/Set
MOQ1 Set/Sets
Product TypePellet Burner
ConditionNew
TypePellet Burner
Voltagecustomizable Volt (v)
Powercustomizable Volt (v)
Weight (kg)customizable Kilograms (kg)
Zhejiang Meibao Industrial Technology Co., Ltd.
Hangzhou
Heat Furnace - Feature: High Quality
Price Trend: 100000.00 - 1000000.00 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
FeatureHigh Quality
ConditionNew
UsageHeat Treatment furnace
Voltage200-450 Volt (v)
Warranty5 Years
Shafts Vacuum Annealing Furnace
Product DescriptionOwing to our proficiency in this domain, we offer our clients a wide gamut of Vacuum Annealing Furnace. \015\012Capacity 1200 kgs\015\012Working chamber 750 x 750 x 1200 mm\015\012200kw ,Vacuum range 0.01 m bar\015\012Make Degussa ( 1985 )\015\012Temp.- 1000 deg c\015\012Heating and Cooling cycle th
British Super Alloys Pvt. Ltd.
Ahmedabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller13 Years
Latest From Furnace Manufacturers
Heavy Duty Hardening Furnace
By:
Meta Therm Furnace Pvt. Ltd.
Annealing Furnace Manufacturers
By:
M. G. Electricals
Muffle Furnace
By:
Mahadev Scientific
Induction Melting Furnace
By:
Stead Fast Engineers (p) Ltd.
Aluminium Melting Furnace
By:
B. S. Jagdev & Sons
Ladle Refining Furnaces
By:
Electrotherm (india) Ltd.
Tempering Furnaces
By:
Silcarb Recrystallized (p) Ltd.
Electric Furnace
By:
Shreenathji Engineering Works
Heat Treating Furnace
By:
Thermochem Furnaces Pvt. Ltd.
Explore More Cities
Ready To Ship Furnace Manufacturers
What is a furnace?
A furnace is a direct-fired heating appliance used in industries that demand temperatures above 400 degrees Celsius (752 degrees Fahrenheit). An industrial furnace is used in any process that requires high temperatures, such as the generation of a chemical reaction or the heating of raw materials. The most dependable among the many machines and tools used in manufacturing and processing are furnaces. Direct or indirect contact heating is used to bring the temperature of raw materials and finished goods up to the desired level prior to use.
Air and flue blowers, heat exchangers, burners, fuel control, a pilot or ignition mechanism, control circuits, and a thermostat are all components of a furnace's build. Even though these are standard features, there are many other furnace designs to choose from depending on the task at hand.
Types of furnace
1. Rotary Tube Furnaces
Due to their versatility and ability to apply heat in different thermal control zones, rotary tube furnaces are frequently employed for continuous material processing.
These furnaces have a wide range of applications, from clinker and alumina production to oxidation.
2. Tensile Testing Furnaces
Material properties such as ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, strain-hardening, and many more can be determined with the help of a tensile testing furnace.
Quality control testing often involves using special furnaces that apply controlled tension on samples until they break.
3. Sintering Furnaces
Sintering furnaces are used to increase the strength, transparency, thermal conductivity, or electrical conductivity of a material while decreasing its porosity.
Sintering is the process of making a solid mass of material through the application of pressure or heat without completely melting the sample.
4. Annealing Furnaces
The purpose of an annealing furnace is to heat a material and keep it at that temperature until it has cooled sufficiently. It's possible that different cooling rates and temperatures will be used for different tasks.
To improve its cold workability, machinability, and mechanical and electrical properties, a sample can be annealed in a heat treatment procedure.
5. Tempering Furnaces
Due to the potential for excessive hardness, stress, and brittleness following hardening or quenching, iron-based alloys are commonly tempered in a subsequent furnace. During tempering, steel is heated to a certain temperature before being slowly cooled in air.
The amount of hardness lost while heating metal depends on the temperature used.
6. Calcination Furnaces
In most cases, most Furnace Manufacturers suggest a calcining furnace is used to either recover the base material after another process has been performed, or to prepare raw materials for further processing.
A calcination is a form of heat treatment in which a sample, such as a mineral or ceramic powder, is heated to a temperature over its critical temperature but below its melting point in order to bring about a phase transition, thermal breakdown, or the removal of a volatile portion.
7. Ashing Furnace
A sample is burned in an ashing furnace, which measures the amount of ash that is produced. Petroleum compounds, lubricating lubricants, and coal are common ash samples utilized in these furnaces.
When ash is created, this method is commonly used to determine the presence of pollutants in the sample.
Before doing chemical analysis, ash is often used as a preconcentration technique to identify any lingering impurities.
8. Blast Furnaces
Blast furnaces can take the form of tall cylindrical structures or towers with special linings designed to withstand extremely high temperatures. By doing so, they drive gases and hot air through the furnace's contents.
The ore, fuel, and limestone go through a chemical reaction as they move down the cylinder and are pushed out the top of the furnace by the incoming air.
9. Electric Furnaces
To generate high temperatures, an electric furnace makes advantage of electrical resistance. They are made out of a variety of materials that can withstand high temperatures.
The temperature of the materials, gas, or air being heated is monitored by a sensor located outside of the enclosed enclosure.
Electric heaters may be set to a fixed temperature or allowed to fluctuate. Coal and oxygen can be added to boost the stove's temperature.
10. Gas Furnaces
With the ever-increasing cost of energy, gas-fueled furnaces have become a more financially viable option.
Gas furnaces are categorized by their condensing efficiency, which must be at least 90%, and their annual fuel usage efficiency (AFUE), which is the percentage of fuel converted into usable heat.
11. Induction Furnaces
To heat metal, induction furnaces combine the effects of electrical resistance and hysteresis losses. When compared to other types of furnaces, they are cleaner and use less energy.
12. Vacuum Furnaces
To reduce the likelihood of unwanted surface reactions, vacuum furnaces function in an airtight, vacuum environment. Contamination is prevented by the absence of air and gases.
Vacuum furnaces are able to braze, sinter, and heat-treated metals under consistent and precise circumstances due to the high temperatures they can reach.
Working principles of a furnace
There are two ways to generate the furnace between two electrodes:
- High Tension (HT) method
- Low Tension (LT) method
1. HT Method
H. T. furnaces are created by keeping a constant air gap between two conducting electrodes. The electrodes are linked to the step-up transformer's high-voltage secondary winding, while the primary winding is supplied with a controllable alternating current.
Now, the voltage across the high tension secondary winding—and hence across the electrodes—must be raised progressively in order to strike an electric furnaces. The medium between the electrodes is ionized and becomes conducting at a specific voltage.
The electric furnace is formed between the electrodes at this point. Because the resistance of the conducting gap between the electrodes is so much lower than that of the air gap after striking the furnaces, the voltage across the electrodes must be lowered from its high-tension (H. T.) value to its low-tension (L. T.) value. The air gap between the electrodes determines the minimum H. T. voltage needed.
2. LT Method
A schematic representation of the L. T. method of electric arc striking. When using this technique, an furnaces can be formed between electrodes with a relatively low voltage, on the order of the supply voltage. The step-down transformer's low-voltage secondary winding is linked to the two conducting electrodes in this technique.
A furnace is created when a brief short circuit is made between these electrodes, followed by their instantaneous separation.
Uses of furnace
1. Atmospheric Controlling
The industrial furnace can be run in either a conventional environment (with the tube furnaces) or an inert atmosphere (with the gas-sealed box furnaces). The furnace has fast cooling and heating rates, consistent temperature control, a small footprint, and a robust build, making it one of the most trusted and commonly used lab furnaces on the market. At high temperatures, these furnaces won't hot spot, and they're durable.
2. Thermal Cycling
High-purity alumina fiber is used in the graded insulating package used in furnaces. Since this insulation has low heat conductivity and is lightweight, extremely rapid thermal cycling is feasible. At high temperatures, these furnaces won't hot spot, and they're durable.
3. Metallizing
These metal-melting furnaces come in a range of sizes to accommodate a variety of applications and output rates. Furnaces are still actively engaged in this activity. It didn't take long for us to progress from metalizing to co-firing multilayer ceramic packaging. The furnaces series includes anything from little benchtop models to massive, factory-wide installations.
4. Brazing
Features such as various zone controls, wax or binder removal sections, low or high dewpoint features, preheat section, and a turn-key automated pusher is included to accommodate applications such as brazing.
5. Calcining
Furnaces are trusted and commonly used calcining devices. You can heat or cool something quickly with them, and they have precise temperature regulation, a small footprint, and a durable design to last for years.
6. Sintering
A furnace provides debinding and sintering capabilities in their batch environment furnaces, making them ideal for process development and low-volume production runs. The furnaces are economical to run. They're built to last and require almost no upkeep to keep functioning well.
7. Annealing
When it comes to processing wire, rod, strand, strip, and tube products, the continuous annealing furnaces are built to last for years with no maintenance. Copper alloys, stainless steel, nickel, nickel chrome, Copper, titanium, and refractory metals are most suited for use in these furnaces.
From the manufacture of plastics to the deformation of metals, industrial furnaces have become indispensable. Many of the things we use every day have been heated in a factory oven before they reached the tables. Industrial furnaces have been a major source of the problem for decades, if not centuries. Manufacturers and consumers alike are constantly working to enhance industrial furnace operations in order to mitigate their shortcomings.
FAQs: Furnace
Q. What is a furnace used for?
Ans. Warm air is pumped through the house via ducts from the furnace. Water boilers produce either hot water or steam for use in space heating.
Q. Does the furnace need water to run?
Ans. No, while water heaters serve the same purpose, furnaces do it without the need of water. Furnaces, on the other hand, use combustion gas produced by natural gas burners to heat the air; no water is used in this process.
Q. Is a furnace only for heat?
Ans. All heaters can be thought of as furnaces, but not all furnaces can be thought of as heaters.
Q. How does a furnace work in a house?
Ans. Your furnace's burner lights the gas once it has been drawn from a tank (for liquid propane) or the local gas distribution system (for natural gas). The heat exchanger in your furnace is where the cold air from your home is heated by the burning gas.
Manufacturers & Suppliers of Furnace Manufacturers
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Ugi Engineering Works Pvt. Limited Kolkata, India | 21 Years |
Classic Scientific Boisar, India | 21 Years |
Ashlyn Chemunnoor Instruments Pvt. Ltd. Thrissur, India | 17 Years |
Standard Steel Ambala Cantt, India | 17 Years |
Steelfab Industries Vasai, India | 16 Years |
Meta-Lab Scientific Industries Mumbai, India | 16 Years |
Shapet Induction Private Limited Rajkot, India | 16 Years |
Eie Instruments Private Limited Ahmedabad, India | 15 Years |
Bioline Technologies Thane, India | 14 Years |
Southern Scientific Lab Instruments Private Limited Chennai, India | 14 Years |
Popular Products