Insulation Material
(4550 products)Metasteel Prefab Private Limited
Gandhinagar
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Premium
Super Premium Premium Seller
Premium Seller5 Years
 Super Premium
Super PremiumAcoustic Insulation Jackets Application: Plants Operating At High Temperatures
Price Trend: 5000.00 - 6000.00 INR/Square Meter
MOQ100 Square Meter/Square Meters
Density100-1000 Kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
Product TypeJackets
MaterialFiberglass
Width600 Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationPlants operating at high temperatures
ColorSilver
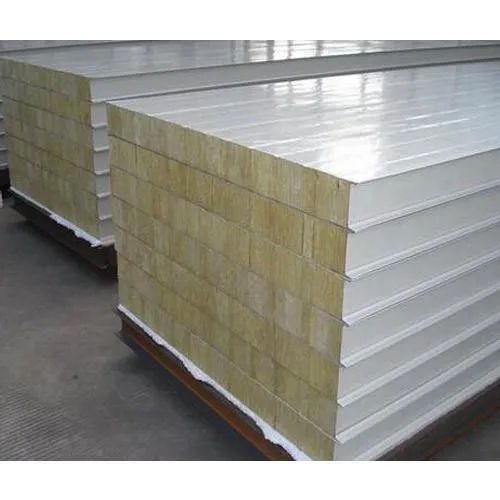
Puf Insulated Panel - Application: Industrial. Commercial & Residential
Price: 1450 INR/Square Meter
MOQ1000 Square Meter/Square Meters
Density40 Kg/Cu.mt to 80 Kg/Cu.mt Kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
ApplicationIndustrial, Commercial
ColorBlue
Product TypePuff Insulated Panel
MaterialPUF
Main MaterialSteel
Fiberglass Cloth Application: Transformers
Price: 270 INR/Kilograms
MOQ100 Kilograms/Kilograms
Thickness0.15 / 0.20 / 0.25 / 0.30 Millimeter (mm)
ColorWhite
Length2 Meter (m)
Product TypeInsulation tape
MaterialFiberglass
Width1/2", 3/4", 1", 1.5" 2", 3", 4" Inch (in)
Harnawa Insulations Private Limited
Mumbai
 Super Premium
Super Premium7 Years
 Super Premium
Super PremiumEpoxy Insulator - Application: Industrial
Price: 16.00 INR/Piece
MOQ10000 Piece/Pieces
Product TypeEpoxy Insulator
MaterialFRP
ApplicationIndustrial
ColorRed
Zaral Electricals
Vadodara
 Super Premium
Super Premium10 Years
 Super Premium
Super PremiumThermal Insulation Sheet - PPGI/PPGL Material, 0.45 Thickness , 0.503 Density for Industrial Applications
Price: 400 INR/Square Meter
MOQ100 Square Meter/Square Meters
Density0.503 Gram per cubic meter (g/m3)
Product TypeThermal Insulation Sheet
MaterialPPGI/PPGL
Thickness0.45 Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationIndustrial
Pushpak Infra Steel Private Ltd.
Pune
Flange Insulation Kit - Reinforced Phenolic & Nylon, API/ANSI/DIN Compliant Gasket Types E, F, D
Price: 2000 INR/Piece
MOQ5 Piece/Pieces
Product TypeINSULATING KIT
MaterialMetal
ApplicationIndustrial
ColorAll Color
Color Coated PUF Insulated Cement Sheet Wall Panel
Product DescriptionColor Coated PUF Insulated Cement Sheet Wall Panel
Supreme Hvac Insulation Material - Application: Industrial
MOQ10 , Piece/Pieces
Product TypeSupreme HVAC Insulation Material
Rated Voltage220 Volt (V)
ApplicationIndustrial
ColorGray
The Supreme Industries Ltd.
Mumbai
 Super Seller
Super Seller8 Years
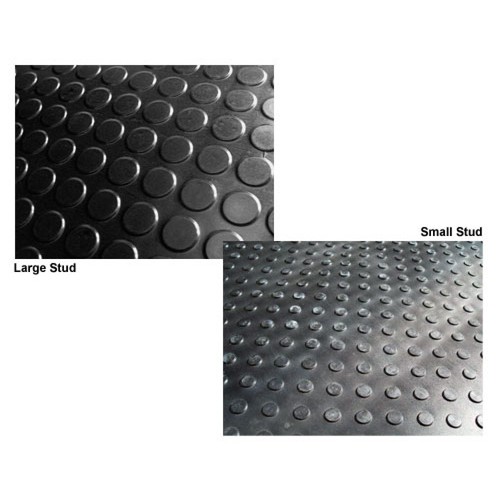
Sea Green Electrical Insulated Rubber Mats
Price: 300.00 INR/Piece
MOQ500 Piece/Pieces
ColorSea Green
Product TypeElectrical Insulated Rubber Mats
MaterialRubber
Thickness2.5 Millimeter (mm)
Softex Industrial Products Pvt. Ltd.
Kolkata
 Super Seller
Super Seller18 Years
Insulation Rubber Mats - Application: Industrial
Price: 590 INR/Piece
MOQ1 , Piece/Pieces
ColorBlack
Product TypeInsulation Rubber Mats
MaterialInsulation Rubber
Thickness6-25 Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationIndustrial
Ameenji Rubber Limited
Secunderabad
Thermal Insulation Boards - Application: Industrial
MOQ1000 Piece/Pieces
Product TypeThermal Insulation Boards
MaterialXPS Board
Thickness25, 30, 50, 75 Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationIndustrial
ColorMulticolour
Aditya Packaging & Consulting Service Pvt. Ltd.
Pune
Press Board Strips - Cork Material, Insulating and Non-Corrosive Surface | Accurate Dimensions, Easy Installation, No Carbon Accumulation
MOQ100 Piece/Pieces
Product TypePress Board Strips
MaterialCork
PUF Insulated Panels - Polyurethane Foam, 40 to 150 mm Thickness | High Thermal Resistance, Energy Efficient, Versatile Wall & Roof Application
Price Trend: 1500.00 - 5000.00 INR/Square Meter
MOQ50 Square Meter/Square Meters
Density40 Kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
MaterialPolyurethane Foam
Thickness30 to 200
ApplicationWall & Roof
Krishna Insulations & Engineers Pvt Ltd
Vadodara
 Super Seller
Super Seller15 Years
Hvac Insulation Material
Price: 800 INR/Piece
MOQ100 Piece/Pieces
Product DescriptionHvac Insulation Material
Reflective Insulation - Color: Silver
Price: 1000 INR/Square Meter
MOQ1 Square Meter/Square Meters
ColorSilver
Product TypeReflective Insulation
ApplicationInsulation
Woven Polyester Tape - Application: Industrial
Price Trend: 1.25 - 10.00 INR/Meter
MOQ20000 Meter
Width6 mm to 70 mm Millimeter (mm)
Thickness0.10 mm to 0.50 mm Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationIndustrial
Unitech Insulations & Cables (india) Pvt. Ltd.
Kolkata
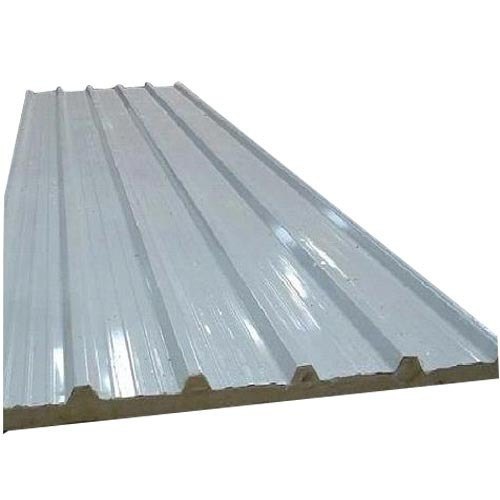
PUF Sandwich Panel - 60 mm Thickness, 1 Meter Width, White Color | Excellent Thermal Insulation, Durability, Fire Resistance
Price: 1600 INR/Square Meter
MOQ100 Square Meter/Square Meters
ColorWhite
Product TypePUF Sandwich Panel
MaterialPUF
Width1 Meter (m)
Thickness60 Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationIndustrial
Sfib-101 Braided
Price Trend: 900.00 - 920.00 INR/Kilograms
MOQ100 Kilograms/Kilograms
Supply AbilityAs per demand Per Week
Delivery Time2-3 Days
Dupont Nomex Paper - Color: White
Price: 4000 INR/Kilograms
MOQ1 Kilograms/Kilograms
ColorWhite
Product TypeDupont Nomex Paper
MaterialNomex Paper
Thickness.25 - 2 mm Millimeter (mm)
PUF Insulated Panels - 12m Length, 30-150mm Thickness | Efficient Cold Room Design for Beverages, Frozen Foods, Dairy Products, and Medicines
Price Trend: 1000.00 - 2500.00 INR/Square Meter
MOQone lot , Square Meter/Square Meters
MaterialOther
Nitrile Rubber Sheet
Price: 800 INR/Unit
MOQ100 Unit/Units
Product DescriptionNitrile Rubber Sheet
Insulated Windows - Application: Home And Hotel
Price: 400 INR/Square Foot
MOQ100 Square Foot/Square Foots
ColorWhite and Brown
Product TypeInsulated Windows
ApplicationHome And Hotel
Solid Core Insulator By Andisc Engineers Private Limited
Price Trend: 1500.00 - 11500.00 INR/Piece
MOQ10 Piece/Pieces
Payment TermsCash in Advance (CID)
Supply Ability1000 Per Week
Delivery Time5-7 Days
Andisc Engineers Private Limited
Kolkata
Hidden Screw Wall Panels - Application: Industrial
Price: 135 INR/Square Meter
MOQ100 Square Meter/Square Meters
Product TypeWall Panels
MaterialPUF
ThicknessDifferent Available Millimeter (mm)
ApplicationIndustrial
ColorOff White, Blue
Elements Technofab Private Limited
Pune
Slitted Insulating Kraft Paper Application: Industry
Price Trend: 500.00 - 2000.00 INR/Kilograms
MOQ1000 Kilograms/Kilograms
Product TypeInsulation Paper
MaterialWood Pulp
ApplicationIndustry
ColorGrey
Signature High Temperature Textile Cloth Temp.1200C - Application: Industrial
Price: 26250 INR/Roll
MOQ1 Roll/Rolls
ColorCream
Product TypeHigh Temperature Textiles
MaterialInsulation
ApplicationIndustrial
Latest From Insulation Material
Explore More Cities
Ready To Ship Insulation Material
Most Common Insulation Material In Industry
Introduction
Fiber materials including fiberglass, natural fibers, rock, slag wool, and cellulose are on the bulkier end of the insulation spectrum, while other options include stiff foam boards and sleek foils. In a building's hollow, bulky materials act as a barrier to both conductive and, to a lesser extent, convective heat flow.
Fiberglass is the most common insulation material in the Industry. Fiberglass, made of microscopic glass strands, is a popular insulator. Insulation blankets loose-fill, rigid boards, (both rolls and batts), and duct insulation all make use of this material.
These days, you may find fiberglass batt insulation in densities that are both somewhat denser and have better R-values than the old standard batts. Cathedral ceilings and other spaces with limited cavity space can benefit from the denser products.
Main Types of Insulator Materials
1. Insulation Facings
During production, insulation materials have their facings attached using fasteners. Facings are used to prevent damage to the insulation's surface, keep the insulation from shifting, and make it easier to attach the insulation to structural elements.
Some facings are also effective as air barriers, radiation barriers, and/or vapor barriers; others offer fire resistance.
If the seams between insulation boards are taped and sealed, then all of these materials will function as a vapor barrier and air barrier.
2. Phenolic Insulation Material
In the past, rigid foam board insulation made of phenolic foam was rather common. Available in board and foamed-in-place forms, its board insulation form is currently in short supply.
Air is used as the foaming agent in blown-in phenolic insulation. The fact that cured phenolic foam might shrink by as much as 2% is a major reason for its declining popularity.
3. Cementitious Insulation
Cementitious insulation is a spray-foam or foamed-in-place insulation made from cement-based foam. Aircrete® is a brand of cementitious spray insulation that has an initial viscosity like shaving cream because it contains magnesium silicate. When a space needs to be sealed, the professionals use air krete®.
Made from minerals (like magnesium oxide) derived from saltwater, cementitious foam is both inexpensive and safe to use.
4. Perlite Insulation Materials
Homes constructed prior to 1950 often have attics insulated with perlite. In order to create perlite, rock pellets are heated until they pop, resulting in very small, lightweight pellets. These results in a concrete that is lighter and less heat-conductive, or even a loose-fill insulating stuff composed of pellets that can poured into place.
5. Polyurethane Insulation Materials
Polyurethane is a low-conductivity gas-filled thermoset foam that is widely used as an insulator. Insulation made from polyurethane foam comes in both closed-cell and open-cell varieties.
High-density cells of closed-cell foam are sealed off and filled with a gas that allows the foam to expand and fill any empty spaces. Since the cells of open-cell foam are not as dense and are filled with air, the insulation has a softer, less dense feel and a lower R-value. It is possible for the R-value of closed-cell polyurethane Insulation Material to decrease with time, much like that of polyiso foam, due to thermal drift or ageing, which occurs when air replaces some of the low-conductivity gas that was previously there.
A material's R-value remains stable unless the foam is damaged, and thermal drift is greatest in the first two years following production.
6. Polyisocyanurate Insulation Materials
Low-conductivity gas is used to fill the closed-cell foam, which is manufactured of thermosetting plastic.
Polyisocyanurate insulation comes in a variety of forms, including liquid, sprayed foam, or rigid foam board. It's also useful for creating laminated insulation panels with customizable skins. Foamed-in-place uses of polyisocyanurate insulation can be more cost-effective than using foam boards due to the insulation's ability to conform to irregularly shaped areas.
7. Polystyrene Insulation Materials
Foam beads are another form of the insulating material molded expanded polystyrene (MEPS), which is more usually seen in foam board form. Although they are useful as pouring insulation for concrete blocks, these beads are famously difficult to regulate due to their small weight, susceptibility to static electricity, and the difficulty of removing the insulation once it has been poured.
8. Cellulose Insulation Material
Cotton, sheep's wool, straw, and hemp are just few of the natural fibers that are put to use in the insulation industry.
- Hemp: In the United States, the usage of hemp insulation is uncommon because of its lack of public awareness.
- Straw: Straw bale building, common on the Great Plains of the United States 150 years ago, is seeing a renaissance.
- Sheep’s Wool: When sheep's wool is treated with borate, it becomes pest-, fire-, and mold-resistant, making it ideal for use as insulation.
- Cotton: Similar to cellulose insulation, cotton insulation is constructed from 85% renewable materials and 15% polypropylene fibers sprayed with carbonate to put out fires and repel pests and mice.
Wall Insulation Materials
For External Wall Insulation:
1. Insulation Layer
The primary insulator, typically mineral wool or expanding polystyrene. In most cases, this is attached to the exterior of the house using self-tapping screws:
Polystyrene features:
- Soft, breathable fabric
- The material has a low heat conductivity and absorption of water.
- High resilience to chemicals and aging
Mineral Wool Features:
- Additive for water resistance is possible.
- Fabric that allows airflow
- Low heat transfer
- Exceptional toughness
2. Glass Fibre mesh
- Made to improve the insulation wall's stability, adaptability, and binding
- Added after the insulation boards but before the final coat of render
- Applied by being pressed into an adhesive mortar and then smoothed over
For Internal Wall Insulation:
1. Stud Wall
Mineral wool is stuffed into a connected metal or wooden studwork frame. Paint or wallpaper can be applied after the surface has been plastered.
2. Rigid Insulation Boards
Rigid insulating material, typically foamed plastic, is adhered directly to the back of plasterboard and then mounted on the interior wall. There are additional fasteners used to keep the boards in place, and the joints are sealed to prevent air leakage.
Cavity wall Insulation:
The three most prevalent types of cavity wall insulation materials are:
1. Blown mineral fibre
Compressed air is used to blow strands of fiberglass or mineral wool into the space. For cavity walls, this is the norm.
2. Polystyrene beads or granules
The granules will either naturally adhere to one another, or a sticky resin will be added to them (beads).
3. Urea formaldehyde foam
The cavity instantaneously filled after two chemical components were delivered at the same time.
Type And Use of Insulation Materials
There are several uses for insulating materials, including
- Transmission lines and cables
- Technology-based Methods
- Electrical grids
- Equipment for use around the house that may be carried with relative ease
- Electric cable insulation tape
- Gear for self-protection
- Rubber floor mats with built-in electric conductors
These days, cellulose, foam, and fiberglass are typically used as insulation. Now spray foam, loose-fill, Batts, and rigid foams are the most commonly used types of insulation. Even though these are the most frequently chosen options, the best choice will depend on your individual circumstances.
There isn't really a "best" insulation available. Each has advantages and disadvantages, and some are better suited to certain tasks than others. What kind of insulation is ideal for your home depends on a number of factors, including your climate, the areas of your home you intend to insulate, the amount of money you have available, and whether or not your home is already built.
FAQs: Insulation Material
Q. What are hot and cold insulation materials?
Ans: Hot Insulation material is made to reduce heat loss for energy efficiency and to shield workers from potentially dangerous temperatures. Reducing heat transfer to pipes, preventing condensation and ice buildup on outside surfaces, and ensuring worker safety are all made possible by cold insulation material.
Q. Best insulation materials suppliers in india?
Ans: Aerolam is one of the best insulation suppliers in India. To be more precise, Aerolam is a multifaceted organization that has manufacturing expertise in FIBC (PP Woven Jumbo Bags), Reflective Insulation Material, and CPP Film Especially for Medical & Food grade Packaging.
Q. What is the cost of insulation materials?
Ans: The price of insulation materials is between Rs 400-5500 square meter in India.
Q. How we can purchase insulation materials in bulk?
Ans: If you’re looking insulation material in bulk, Trade India would be the best place to get ideal deal. Look for the supplier who offers the reasonable and high quality insulation material at Trade India.
Manufacturers & Suppliers of Insulation Material
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Mag Hard Insulators Mumbai, India | 21 Years |
Everest Composites Pvt. Ltd. Vadodara, India | 18 Years |
Softex Industrial Products Pvt. Ltd. Kolkata, India | 18 Years |
Ganpati Engineering Industries Jaipur, India | 16 Years |
Ganapathy Industries Bengaluru, India | 16 Years |
Natraj Insulation Vadodara, India | 15 Years |
Krishna Insulations & Engineers Pvt Ltd Vadodara, India | 15 Years |
Shree Umiya Glass Works Anand, India | 15 Years |
Andisc Engineers Private Limited Kolkata, India | 15 Years |
Ameenji Rubber Limited Secunderabad, India | 13 Years |
Popular Products