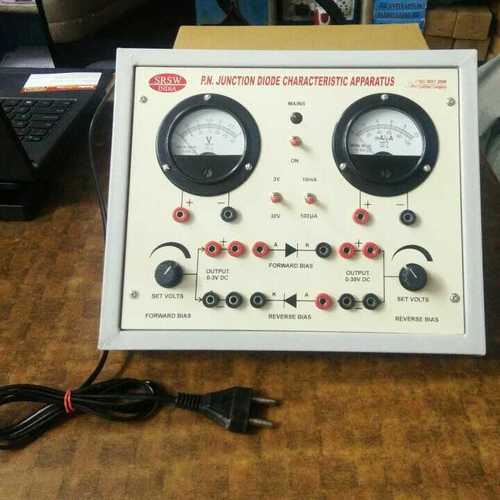
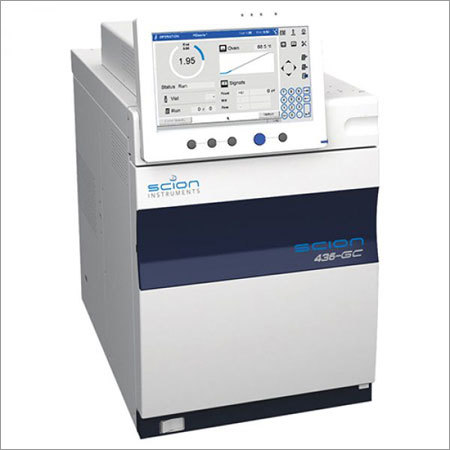
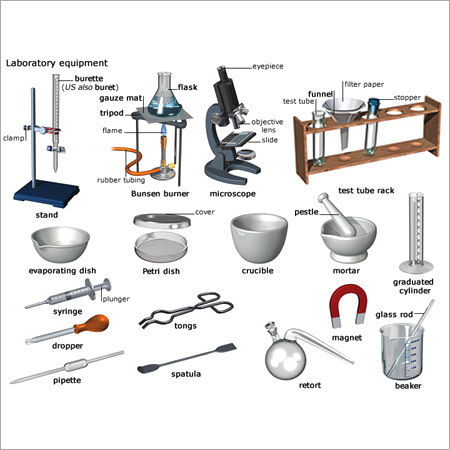
Scientific & Laboratory Instruments
Recently Added Products
What are Scientific Instruments?
Introduction
A scientific instrument's precise legal and cultural definition has evolved over time. Ancient and medieval devices like the astrolabe and the grandfather clock challenge a more modern description of "a tool designed to investigate nature qualitatively or quantitatively." Before the mid-19th century, these equipment were known as "natural philosophical" or "philosophical" apparatus and instruments.
A new level of instrumentation was achieved as a result of the need for better examination of war items like pharmaceuticals, fuel, and weapons-grade substances. Connectivity to computers and data management systems is becoming increasingly important in today's fast evolving scientific community, particularly for analytical instruments.
Different types of Scientific & Laboratory Instruments
1. Burette
It is indispensable for delivering a precise amount of a drug to other devices in titration reactions. In this setup, a long graduated tube with a stopcock at the base serves as the main component. It is often available in 10, 25, and 50 milliliter sizes.
2. Spring balance
Another tool that can be useful when determining an object's mass is a spring balance, often known as a Newton meter. This device, made up of a spring and a hook, operates on the principle of Hooke's law, which states that the force applied to an object is directly proportionate to the extension, within the bounds of the elastic limit.
3. Spatula
These laboratory spatulas look and function similarly to the kitchen spatulas we're used to, but they're much smaller. The spatulas can withstand high temperatures and acidic environments, making them ideal for use in extensive scientific investigations.
4. Weighing Machine
These weighing devices are useful since it is difficult to achieve the correct and precise amounts of the reagents using a regular physical balance. Precision balances and analytical balances are the two main types of lab scales. The most common type of balance is a precision balance that can measure down to the milligram.
Analytical balances, on the other hand, are so delicate that they can be thrown off by the slightest breeze. Because of this, the weighing plate is enclosed within a glass cage. Analytical scales are accurate to the microgram level.
5. Brushes
One of the largest components of daily life in the lab is cleaning, which is often overlooked. The first step toward accuracy and precision is meticulously maintaining all equipment and glassware.
6. Tongs
A pair of tongs is standard issue in each laboratory, but they rarely see action. They are needed for handling dangerous chemicals and heated containers in the course of any laboratory reaction.
7. Thermometer
Despite the availability of digital thermometers, the analog varieties remain the ones most commonly used in scientific settings.
8. Dropper
The dropper is a popular little equipment that consists of a plastic or glass cylinder with a tiny nozzle on one end and a rubber holder on the other.
9. Bunsen burner
A single open flame is produced by this piece of equipment and is put to use in a wide variety of laboratory investigations requiring either heating or sterilizing. Bunsen burners were designed specifically for the task of heating and boiling the many items that must be done in a laboratory. In contrast to a spirit lamp, it uses normal LPG fuel and can get quite hot.
10. Volumetric Flask
An absolute necessity in any laboratory, this glassware may be adjusted to retain a specific volume of liquid at a given temperature. Various sized volumetric flasks are available for precise measurements of liquids and solutions.
11. Magnifying Glass
When light is refracted through a magnifying glass, a magnified image is created virtually. Magnifying glasses rely on a convex lens, a round piece of glass that is thick in the middle and tapers to thin edges.
12. Beakers
Similarly to measuring cups, beakers are glassware containers that are cylindrical in shape and have a flat bottom and an upper opening that may or may not have a spout. They come in a wide range of sizes and are used to store, heat, and blend various chemicals.
13. Microscope
The biology lab would be completely useless without a microscope. The type of microscope most commonly found in classrooms is the basic light microscope (compound microscope), which magnifies an object by using both natural or artificial light and a series of lenses.
Difference between Laboratory Equipment and Laboratory Instruments?
Instrument
- Flow, pressure, weight, and so on are only some of the units that may be measured with the help of various instruments. One piece of machinery is the instrument.
- The term "instrument" is commonly used to refer to a sensor (a type of measuring instrument) like a thermometer or hygrometer.
Equipment
- The term "equipment" refers to a collection of tools used for a specific purpose.
- Equipment: a wide variety of equipment like a water bath, oven, or incubator that are typically wired to an electrical source.
One example of an instrument is a resistance temperature detector (RTD) or thermocouple, both of which are used to measure temperatures. Equipment, on the other hand, refers to a collection of instruments or parts of instruments that work together to execute a certain duty, such as an RTD as well as a temperature indicator and recorder that work together as a system.
Laboratory Equipment Market Size (2022 to 2027)
1. Market Size
During the years 2022-2027, the market for laboratory automation in India is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 9.49%. With the unknowns of the COVID-19 virus in mind, researchers are continually tracking and evaluating the direct and indirect impacts of the pandemic on numerous end use sectors. The study recognizes the significance of these findings to the industry.
Enhanced healthcare infrastructure and the proliferation of hospitals and clinics equipped with cutting-edge labs are the primary factors propelling growth in India's Laboratory & Scientific Instruments industry. The increasing need for healthcare services is another factor driving the industry forward.
Accurate diagnosis, worker safety, reduced reagent volumes, and reduced sample volumes are only few of the benefits of laboratory automation. There has been a beneficial effect on market development from the rising number of clinical studies and the increasing number of drugs that have been discovered.
2. Market Segmentation
Trends in India's laboratory automation market by subsegment, with projections for the years 2022 and 2027 at both the national and regional levels.
By Type:
- Modular Automation
- Whole lab Automation
By Software and Equipment type:
- Automated Drug Discovery laboratory System
- Automated Clinical Laboratory System
- Robotic Systems
- Plate Readers
- Workstation
- Storage Retrieval Systems
By End User:
- Research and Academic Institutes
- Hospitals and Diagnostic Laboratories
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Companies
By Region:
- South India
- East India
- North India
- West and Central India
3. Market Growth
Market expansion is being fueled by factors such as the rising prevalence of time-saving methods, public efforts, private finance, and the increased use of analytical equipment. The expansion of the laboratory equipment services market is being stymied by a number of issues, including the increased focus on reducing the cost of treatments, the mounting demand on pharmaceutical companies to decrease marketing expenditures, and the skyrocketing rates of service contracts.
Conclusion
Students who plan to work in a scientific field should prepare themselves to do a lot of hands-on work and experimentation. Without having done any experiments in class, it would be quite difficult to make the transition from reading about the sciences to putting them into action. With the proper science lab equipment, students can put what they've learned in the classroom into practice. They can do intriguing experiments and observations instead of boring note taking. Learning by doing this kind of thing is a great way to get a grasp on abstract ideas.
FAQs: Scientific & Laboratory Instruments
Q. What is Scientific Equipment?
Ans. By "scientific equipment," we mean anything from models to instruments to machinery used only in the pursuit of scientific knowledge or the instruction of future scientists.
Q. What are the Uses of Common Laboratory Instruments?
Ans. Here are the uses of common laboratory instruments:
- Test Tube uses a container that is perfect for containing and heating up test samples of chemicals.
- Test tube holders are used to heat up test tubes.
- Test tube rack serves as a resting place for test tubes during reactions or while they are not in use.
- Top with wings used to generate a wide flame capable of heating a wide area and bending glass smoothly and without cracks.
- A volumetric flask is a measuring device used to create uniform solutions of known volume.
- Attaching test tubes and other glassware to a ring stand is a simple matter of using a utility clamp.
- A thermometer can be used to determine the temperature of anything from a solid to a gas.
Q. What are examples of Scientific Instruments?
Ans. Bolometer, Carburettor, Calorimeter, Binocular and others are some examples of Scientific instruments.
Q. What is the Difference between Laboratory Equipment and Laboratory Instrument?
Ans. Quantities such as flow, pressure, weight, etc. are measured with the help of various instruments. An instrument is a type of instrumentation. When we talk about equipment, we're usually referring to a collection of tools used for a specific task.
Q. Why are Laboratory Instruments Important?
Ans. Students can learn how to conduct experiments with the use of lab equipment found in classrooms. Many pupils wouldn't be able to get so involved or remember so much without adequate classroom science equipment. Therefore, students can take an active role in their learning and grow in their understanding of the scientific method.
Popular Products
Human HairForklift TrucksServo Voltage StabilizerBasmati RiceBackhoe LoaderCarry Bag Making MachineDrum LifterElectric StackerScissor LiftsIndustrial Vibrating ScreenRotameterFlowmeterRotary Air CompressorIndustrial Eto SterilizerRice Packaging MachinesShredding MachineHammer MillAutomatic Labelling MachineDiesel ForkliftAerial Work PlatformStorage Rack SystemEpoxy ResinMild Steel BarStainless Steel SheetsStainless Steel StripsBag Filling MachinesAsphalt PlantsSlat ConveyorOintment PlantPlanetary MixersLadies KurtisLed LightsCctv CameraBall ValveAnti Cancer MedicineAir CompressorIncense SticksSolar LightsGoods LiftsVitrified TilesStainless Steel CoilsPvc PipesPvc Pipe FittingsUpvc PipesUpvc Ball ValvePipe Elbows